Which work scenarios are more suitable for deploying co-robots?
Date:2020-12-01When it comes to automation, it's hard to skip co-robots. Since its inception more than ten years ago, co-robots have undertaken the automation tasks of many enterprises, and have the safety and flexibility that traditional robots cannot match. This has given motivation to many manufacturers. Global manufacturers initially regarded it as an experimental product: only buy one or two at a time, and then send it to the test shop, rather than putting it into a real production plant. Nowadays, co-robots have been used in all walks of life, and there are working figures all over the world.

When considering the introduction of automation in manufacturing companies, where should we start to make it easier to succeed? Although the needs of each company are different, the manufacturer should first consider the following five work scenarios.
1. What tasks need workers to wait for the process to complete?
Generally speaking, if workers need to wait for the process to be completed before proceeding to the next step, a lot of time and cost will be wasted.
2. Which tasks are too simple for workers?
For example, put parts in boxes, place parts on CNC machine tools, transfer parts from one line to another, insert screws, load/unload rotary indexing tables. If co-robots can do these tasks, why not liberate employees to engage in more valuable work?
3. Which tasks can be broken down into multiple subtasks?
The workflow may contain multiple steps. Sometimes, to reduce the sense of boredom at work, companies will let employees complete the entire work process from start to finish, but the fact is that a series of boring tasks add up to boring. Unlike humans, robots are most willing to perform one or two tedious repetitive steps in the workflow.
4. What kind of position employees often look sad at?
If some employees often show boredom, frustration, or indifference, their value cannot be fully utilized.
5. Which tasks do not require high finger dexterity?
Humans have a pair of dexterous hands, they can complete many complex tasks. At present, many robots can only use a simple vacuum chuck to grip objects and parts with two fingers. If a task requires very dexterous fingers to complete, it is not suitable for the use of robots.
Co-robots and traditional industrial robots are two major categories of automation, and they can meet different production requirements. So how to choose between the two when introducing an automated production line? We have made a quick reference table so that you can easily compare the advantages and disadvantages of co-robots and traditional industrial robots and make trade-offs.
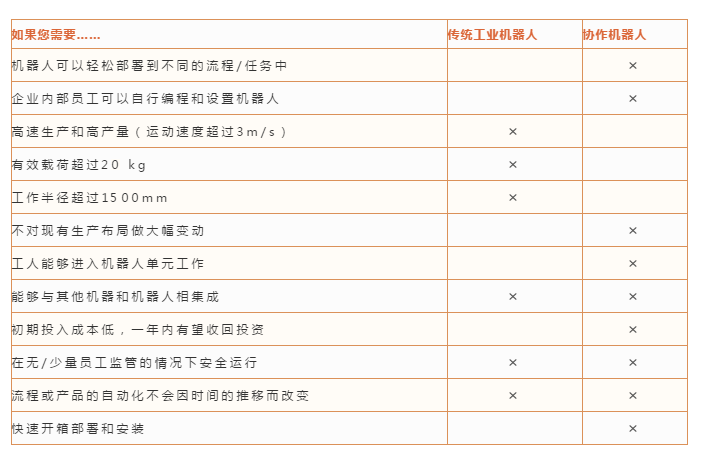
Co-robots are lightweight, easy to deploy, simple to program, and easy to operate. In the future, collaborative robots will become powerful industrial tools.