Cause Analysis of Motor Replacement by Reducer for Robot Joint Motion Control
Date:2019-09-26
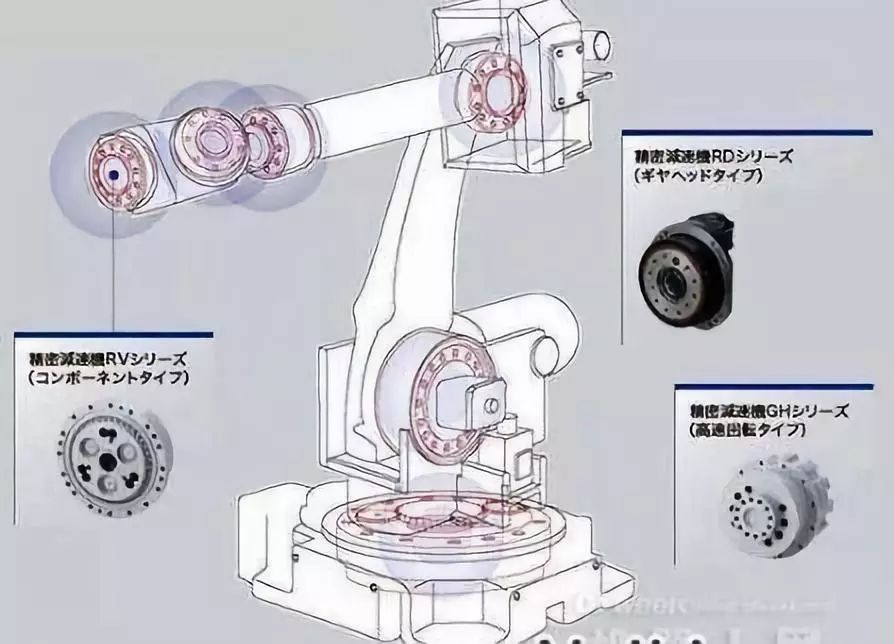
From the structure diagram of the robot arm, we can see that there are motors and speed reducers installed at the joints of the robot to control the joint movement. Then the problem arises:
In the robot system, why can't we directly control the speed of the servo motor rotor to control the joint movement? Why do we need a reducer?
To answer this question, first of all, the working conditions of industrial robot joints should be defined.
1. Joints of industrial robots need to support the torque generated by gravity in the back-end mechanism.
2. The joint speed of industrial robot is not high. Robot joint angular speed is very low, but the motor rotation is not stable at very low speed, and the control is not easy. A machine is needed to make the motor move at a reasonable speed to ensure smooth motion.
Then there are two reasons for using the reducer, the first is to raise the torque, the second is to improve the control resolution and closed-loop accuracy.
For example, a 50:1 harmonic reducer can easily raise the rated torque of a motor rated at 100mNm to 5Nm at the cost of:
1. Rotor speed is 49 times higher than that of direct drive.
Originally, the joint speed of industrial robots is not high, usually one or two revolutions per second. The motor rated 100 mNm can run easily for 6 krpm/min, but not so fast in white. If the suspected rotation is not fast enough, the solution is to raise the voltage, but it is to consider whether the bearing and rotor can hold up.
2. Raise the weight three times as much as before.
For example, the thickest motor of Maxon EC45 has rated torque of 83 mNm and weight of 110 g, while Maxon EC90 has rated torque of 560 mNm and weight of 600 G. From these two data, we can make up the weight of motor rated 5Nm by computer.
3. When the same torque is maintained, the heating power is 1/2500 of that of the non-accelerator-decelerator.
Actually, it's not that the motor rated at 100mNm can't work less than 5Nm, but it can also be done. Just lift the current to death, but this will cause the motor to burn quickly, and smoke in a few seconds, even if it is water-cooled, the electricity bill will be more. If you want to achieve the same torque and do not want to be too hot, you have to change the motor with high torque/heating efficiency, low thermal resistance and large thermal capacity, but this will go back to the problem mentioned in 2.
In addition, the advantages of using the reducer are:
1. Achieving higher resolution with cheaper machinery
An ordinary 5k-line photoelectric code disc can achieve an angular resolution of 1.44 mdeg (of course, if too much money is spent on sine-cosine encoder subdivision can also be achieved); or a 5-phase 1000-step stepper motor can achieve a resolution of 7.2 mdeg (in this case, the 33-step plus 50:1 harmonic of Oriental Motor). The advantage of high resolution is that the speed control can be more precise, and the high frequency component generated by the step caused by quantization becomes smaller and the control is smoother.
2. Improving the Closed-loop Accuracy and Better Control Loop
Because of a large speed reduction ratio of 50:1, the output shaft of the reducer is disturbed and transmitted to the motor end by 37 dB less than that of the direct drive, which makes the closed-loop precision appear higher in the output shaft of the reducer. At the same time, the equivalent moment of inertia of the rotor is increased to 2500 times, which makes the lag link of the control loop dominated by the inertia of the rotor, while the rotor is driven by electromagnetic force directly, so the torque lag caused by stiffness is not caused, which is better controlled than direct drive.
In addition to the above technical answers, here is another case to answer this question indirectly from another angle.
A customer's type of lathe is 6150, the chuck is 10 inches (diameter about 250mm) hydraulic chuck. In order to achieve the cutting ability of single side 7 mm, using the low speed and large torque (torque) characteristics of the spindle motor (AC asynchronous motor), a motor with rated speed of 7.5 kW and 1000 rpm is proposed to be selected, and 1:2 transmission ratio (deceleration) is used at the same time. Gears.
It is known that the transmission ratio is proportional to the power and torque. Even with a 1:2 transmission ratio, the 7.5 kW motor achieves 15 kW and 2 times the rated torque (note that this is not a 2 times rated torque). If you choose a 15 kW motor, the price will be much more expensive, and the installation size will also be larger; and processing a pair of gears with 1:2 transmission ratio does not require a lot of money.
If you don't understand it, you can see the power and torque characteristic curve of the asynchronous motor below. (Note: Unlike DC motors, asynchronous motors may work beyond the transverse torque region.)
In addition to obtaining low-speed, high-torque characteristics, DC motors used on robots may also have this reason, and the transmission ratio of the reducer used may be larger (two-stage drive or higher).
 Of course, the use of reducer is not perfect, there are still some shortcomings, but, by comparison, the use of reducer is more appropriate.
Of course, the use of reducer is not perfect, there are still some shortcomings, but, by comparison, the use of reducer is more appropriate.
Disadvantages of using reducer:
1. If the reducer is equipped and the encoder is installed at the motor end, the manufacturing accuracy of the reducer will affect the actual accuracy.
2. Small errors such as the change of clearance oil film thickness in multi-stage reducer will result in the decrease of repetition accuracy after multi-stage amplification.
3. After all, the reducer has gear meshing or flexible wheel deformation, and has life limitation.
4. The non-linear coupling of the backlash of multi-link mechanism makes the absolute accuracy of the robot poor, so the industrial robot only talks about repetitive positioning accuracy, not absolute accuracy, which makes it difficult for the robot to program purely offline, and improves the difficulty and cost of deployment.
These are the reasons why the speed of the servo motor rotor can not be directly controlled to control the joint movement, but the need to use the reducer. Although there are direct-drive motor-driven robots, due to the above problems, the maturity is still poor.
In the robot system, why can't we directly control the speed of the servo motor rotor to control the joint movement? Why do we need a reducer?
To answer this question, first of all, the working conditions of industrial robot joints should be defined.
1. Joints of industrial robots need to support the torque generated by gravity in the back-end mechanism.
2. The joint speed of industrial robot is not high. Robot joint angular speed is very low, but the motor rotation is not stable at very low speed, and the control is not easy. A machine is needed to make the motor move at a reasonable speed to ensure smooth motion.
Then there are two reasons for using the reducer, the first is to raise the torque, the second is to improve the control resolution and closed-loop accuracy.
For example, a 50:1 harmonic reducer can easily raise the rated torque of a motor rated at 100mNm to 5Nm at the cost of:
1. Rotor speed is 49 times higher than that of direct drive.
Originally, the joint speed of industrial robots is not high, usually one or two revolutions per second. The motor rated 100 mNm can run easily for 6 krpm/min, but not so fast in white. If the suspected rotation is not fast enough, the solution is to raise the voltage, but it is to consider whether the bearing and rotor can hold up.
2. Raise the weight three times as much as before.
For example, the thickest motor of Maxon EC45 has rated torque of 83 mNm and weight of 110 g, while Maxon EC90 has rated torque of 560 mNm and weight of 600 G. From these two data, we can make up the weight of motor rated 5Nm by computer.
3. When the same torque is maintained, the heating power is 1/2500 of that of the non-accelerator-decelerator.
Actually, it's not that the motor rated at 100mNm can't work less than 5Nm, but it can also be done. Just lift the current to death, but this will cause the motor to burn quickly, and smoke in a few seconds, even if it is water-cooled, the electricity bill will be more. If you want to achieve the same torque and do not want to be too hot, you have to change the motor with high torque/heating efficiency, low thermal resistance and large thermal capacity, but this will go back to the problem mentioned in 2.
In addition, the advantages of using the reducer are:
1. Achieving higher resolution with cheaper machinery
An ordinary 5k-line photoelectric code disc can achieve an angular resolution of 1.44 mdeg (of course, if too much money is spent on sine-cosine encoder subdivision can also be achieved); or a 5-phase 1000-step stepper motor can achieve a resolution of 7.2 mdeg (in this case, the 33-step plus 50:1 harmonic of Oriental Motor). The advantage of high resolution is that the speed control can be more precise, and the high frequency component generated by the step caused by quantization becomes smaller and the control is smoother.
2. Improving the Closed-loop Accuracy and Better Control Loop
Because of a large speed reduction ratio of 50:1, the output shaft of the reducer is disturbed and transmitted to the motor end by 37 dB less than that of the direct drive, which makes the closed-loop precision appear higher in the output shaft of the reducer. At the same time, the equivalent moment of inertia of the rotor is increased to 2500 times, which makes the lag link of the control loop dominated by the inertia of the rotor, while the rotor is driven by electromagnetic force directly, so the torque lag caused by stiffness is not caused, which is better controlled than direct drive.
In addition to the above technical answers, here is another case to answer this question indirectly from another angle.
A customer's type of lathe is 6150, the chuck is 10 inches (diameter about 250mm) hydraulic chuck. In order to achieve the cutting ability of single side 7 mm, using the low speed and large torque (torque) characteristics of the spindle motor (AC asynchronous motor), a motor with rated speed of 7.5 kW and 1000 rpm is proposed to be selected, and 1:2 transmission ratio (deceleration) is used at the same time. Gears.
It is known that the transmission ratio is proportional to the power and torque. Even with a 1:2 transmission ratio, the 7.5 kW motor achieves 15 kW and 2 times the rated torque (note that this is not a 2 times rated torque). If you choose a 15 kW motor, the price will be much more expensive, and the installation size will also be larger; and processing a pair of gears with 1:2 transmission ratio does not require a lot of money.
If you don't understand it, you can see the power and torque characteristic curve of the asynchronous motor below. (Note: Unlike DC motors, asynchronous motors may work beyond the transverse torque region.)
In addition to obtaining low-speed, high-torque characteristics, DC motors used on robots may also have this reason, and the transmission ratio of the reducer used may be larger (two-stage drive or higher).

Disadvantages of using reducer:
1. If the reducer is equipped and the encoder is installed at the motor end, the manufacturing accuracy of the reducer will affect the actual accuracy.
2. Small errors such as the change of clearance oil film thickness in multi-stage reducer will result in the decrease of repetition accuracy after multi-stage amplification.
3. After all, the reducer has gear meshing or flexible wheel deformation, and has life limitation.
4. The non-linear coupling of the backlash of multi-link mechanism makes the absolute accuracy of the robot poor, so the industrial robot only talks about repetitive positioning accuracy, not absolute accuracy, which makes it difficult for the robot to program purely offline, and improves the difficulty and cost of deployment.
These are the reasons why the speed of the servo motor rotor can not be directly controlled to control the joint movement, but the need to use the reducer. Although there are direct-drive motor-driven robots, due to the above problems, the maturity is still poor.

Previous Article: Principles of robot control
Next Article: In 2025, the market of cooperative robots will reach 11.5 billion US dollars
